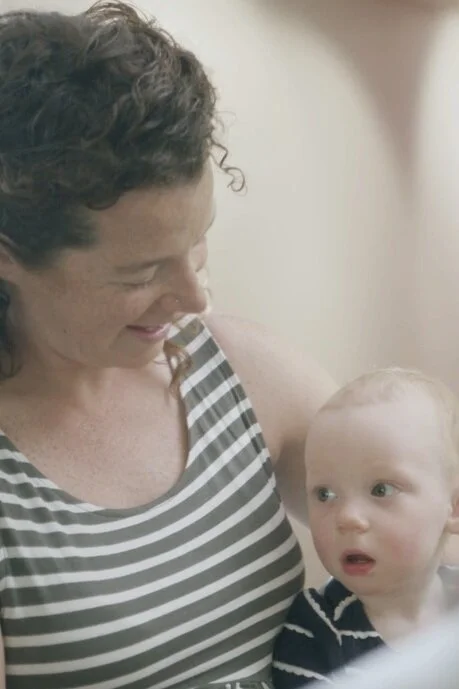
Nourishing Both Mom and Baby: Understanding Relative Energy Deficiency in Sport (RED-S) in Postpartum Breastfeeding Recovery
Welcoming a new life into the world is a beautiful and transformative experience, but it also comes with its challenges.
Among the many considerations during this time, breastfeeding is often a top priority for new moms. However, the journey of breastfeeding and postpartum recovery can be complex, and for some mothers, the path of breastfeeding intersects with another complex issue: relative energy deficiency (RED-S).
This month, as we celebrate Mother’s Day, we are bringing attention to the demands on a mother’s body as she navigates her physical postpartum recovery and transforms into a new mother with nutritional demands beyond her own.
Understanding Relative Energy Deficiency in Sport [RED-S]
RED-S is a condition characterized by low energy availability relative to the energy demands of the body. It can affect individuals across various stages of life, including postpartum women. While the term was initially coined in the context of athletes, its principles apply to any individual experiencing a mismatch between energy intake and expenditure.
Several studies on RED-S and Breastfeeding Recovery have shed light on the relationship between energy deficiency and breastfeeding success, highlighting the importance of proper nutrition and self-care during the postpartum period:
Impact on Milk Production:
A study published in the journal, Nutritionists found that maternal energy intake significantly influences milk volume and composition. Mothers experiencing energy deficiency may produce less milk.Maternal Health and Recovery:
The postpartum period is a critical time for maternal recovery, both physically and emotionally. Research published in the International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health suggests that energy deficiency can prolong postpartum recovery, increase the risk of complications, and contribute to fatigue and mood disturbances.Breastfeeding Duration and Success:
A longitudinal study conducted by researchers at the University of Granada found that mothers with inadequate energy intake were more likely to discontinue breastfeeding earlier than those with sufficient energy availability.
Here are some strategies to consider:
1. Prioritize Nutrient-Dense Foods:
Focus on consuming a balanced diet rich in whole grains, lean proteins, healthy fats, fruits, and vegetables to meet energy and nutrient needs. Incorporating foods that support lactation, such as oats, flaxseeds, and leafy greens, can further enhance milk production.
2. Monitor Energy Intake and Expenditure:
Pay attention to hunger cues and ensure adequate calorie intake to support lactation and recovery. It's essential to strike a balance between energy expenditure, including caregiving and breastfeeding, and energy intake to prevent depletion. This becomes even more critical for women attempting to return to their previous physical activity levels, while also committing their maternal energy to breastfeeding.
3. Seek Professional Support:
Consult with healthcare providers, including lactation consultants and registered dietitians, for personalized guidance and support. Let us work with you to assess individual energy needs, provide tailored nutrition recommendations, and address any concerns related to breastfeeding and recovery.
The journey of postpartum recovery and breastfeeding is a unique and deeply personal experience for every mother. By understanding the concept of Relative Energy Deficiency in Sport (RED-S) and its implications for breastfeeding mothers, we can take proactive steps to support maternal health, optimize breastfeeding outcomes, and nurture the precious bond between mother and baby.
Remember, prioritizing self-care and nourishment as a recently postpartum mother can be a significant period of adjustment. As we begin to return to our formal levels of physical activity as well as the daily demands of life nutritional requirements and our physical recovery need to strike a balance.